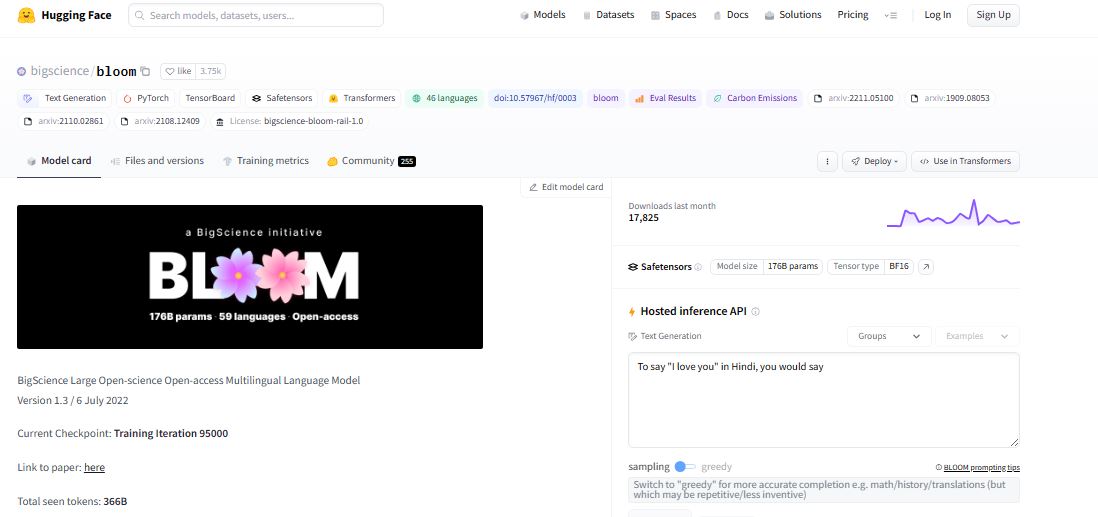
BLOOM, officially known as BigScience Large Open-science Open-access Multilingual Language Model, stands out as a transformer-based autoregressive model with a staggering 176 billion parameters. It represents a significant milestone in natural language processing (NLP) due to its massive scale and open-access nature. Both the model itself and its training resources, including code and data, are distributed under free licenses, fostering accessibility and collaboration in the research community.
The development of BLOOM was a collaborative effort under the BigScience initiative, spanning from May 2021 to May 2022. Led by HuggingFace, this initiative brought together hundreds of researchers and engineers from academia and industry, supported by a substantial public compute grant from GENCI and IDRIS (CNRS). BLOOM was trained extensively on approximately 366 billion tokens, drawn from diverse sources including the OSCAR corpus and meticulously curated language data, covering 46 natural languages and 13 programming languages.
The training corpus for BLOOM, named ROOTS, is a blend of data extracted from OSCAR and newly collected sources. This corpus reflects a wide linguistic diversity, with English comprising the largest portion at 30%, and other languages represented in varying amounts. The meticulous curation of ROOTS ensures that BLOOM’s capabilities extend across a broad spectrum of languages and domains, underscoring its versatility and applicability in multilingual and specialized NLP tasks.