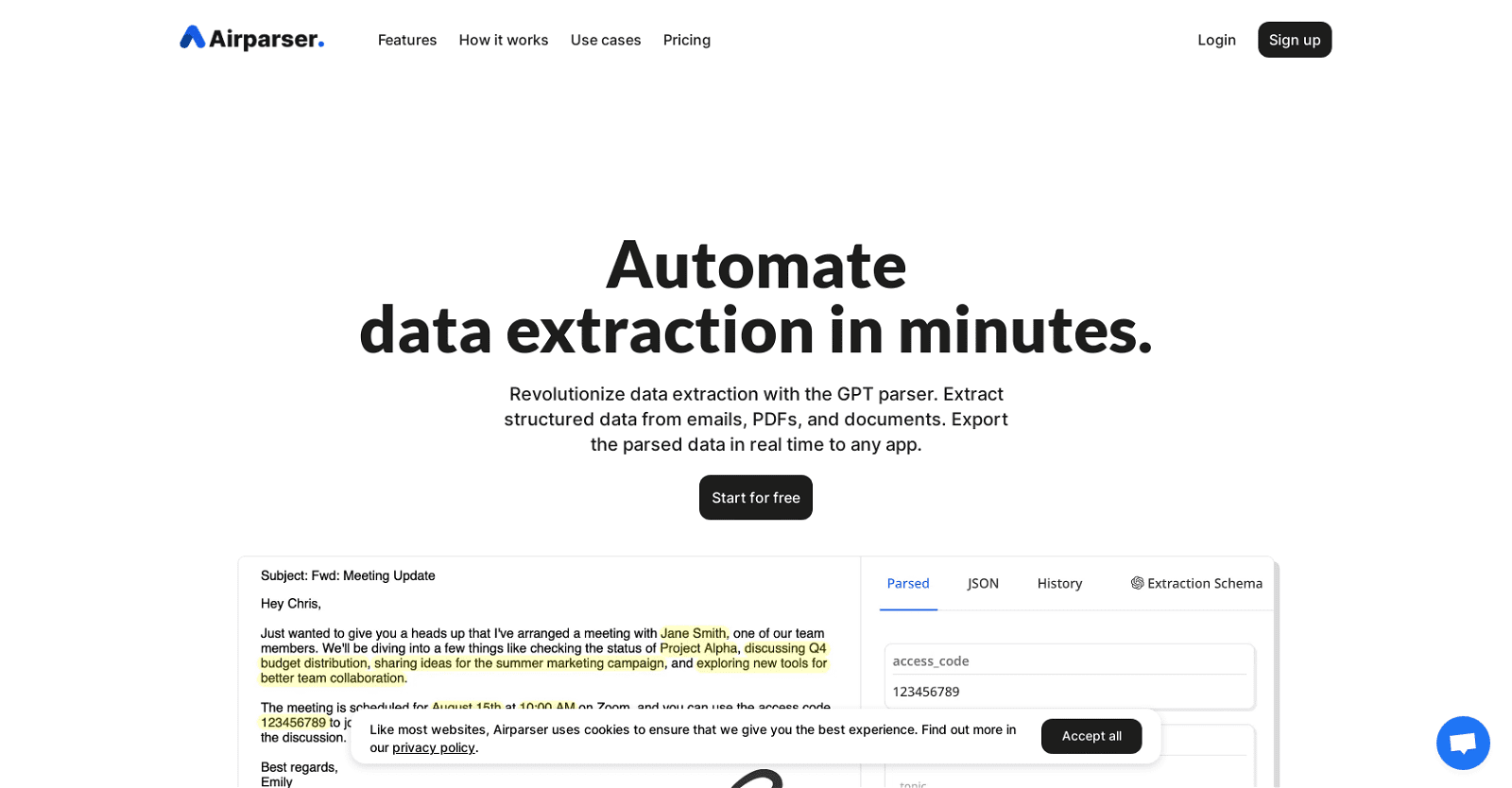
Airparser is a GPT-powered email and document parser tool that revolutionizes data extraction. With this tool, users can easily extract structured data from various sources such as emails, PDFs, documents, and more.
The parsed data can be exported in real time to any desired application. The key features of Airparser include GPT-powered Swift data extraction for efficient results, an OCR engine that seamlessly extracts data from scanned documents, images, and handwritten notes, as well as the ability to parse texts, emails, PDFs, images, HTML, and more effortlessly.
Airparser supports various use cases, including extracting contact information, dates, and key details from human-written emails and texts, digitizing handwritten notes and transforming them into organized data, efficiently capturing details from invoices, receipts, and purchase orders, gathering essential information from CVs and resumes, automatically extracting data from contracts for simplified management, and streamlining order processing by extracting relevant details from confirmation documents.
More details about Airparser
How can I import my files into Airparser?
There are multiple ways to import files into Airparser. You can directly forward emails and attachments to Airparser’s inbox, manually upload your files, or use an automation platform like the API.
Can I extract contact details from CVs with Airparser?
Yes, Airparser can extract contact details, among other things, from CVs and resumes. It helps gather useful details like names, contact information, and work experience seamlessly and efficiently.
Can I extract data from contracts with Airparser?
Yes, Airparser is well-equipped to extract data from contracts. It can automatically pull out terms, involved parties, and other critical data for easy contract management.
How does Airparser extract data from documents?
Airparser uses a combination of AI, the GPT engine, and an OCR engine to extract data from documents. Users describe the data that needs to be extracted, and the GPT-powered parser does the rest.